 Choosing the Right Project Management Approach
Choosing the Right Project Management Approach
Project management methodologies define the success of IT projects. While Agile offers flexibility and adaptability, Waterfall provides structure and predictability. The key to effective IT project execution is selecting the right approach based on project scope, team dynamics, and business objectives.
## Introduction
Choosing between Agile and Waterfall is a critical decision in IT project management. Agile promotes iteration and flexibility, while Waterfall emphasizes structured phases and documentation. Understanding the strengths and limitations of each helps organizations optimize project execution.
## 1. Agile: Flexibility & Rapid Adaptation
Agile methodologies (Scrum, Kanban) enable teams to iterate quickly, making adjustments as needed.
- Best for dynamic projects with changing requirements.
- Focus on collaboration and continuous feedback.
- Delivers incremental value rather than waiting until project completion.
## 2. Waterfall: Structured & Predictable Execution
Waterfall follows a linear approach where each phase is completed before moving to the next.
- Ideal for well-defined projects with fixed requirements.
- Clear documentation & compliance for regulated industries.
- Strong project control with defined scope and timelines.
## 3. When to Choose Agile vs. Waterfall
### Use Agile when:
- Requirements are evolving.
- Speed and flexibility are critical.
- Frequent stakeholder feedback is required.
### Use Waterfall when:
- Project scope is clear and stable.
- Compliance and documentation are key.
- The budget and timeline must be strictly controlled.
## 4. Hybrid Approaches: Best of Both Worlds
Many organizations adopt a Hybrid model, combining Agile’s adaptability with Waterfall’s structure.
- Agile for development phases.
- Waterfall for planning & compliance.
- Ensures both flexibility and predictability.
## Conclusion
No single approach fits all projects. IT leaders must align methodologies with project scope, risk tolerance, and business needs. A well-chosen framework maximizes efficiency, mitigates risks, and drives successful project delivery.
 Future-Proofing Your Data Center Strategy
Future-Proofing Your Data Center Strategy
As IT infrastructure evolves, businesses must rethink their data center strategies to accommodate cloud, hybrid, and on-premise solutions. The future of data centers lies in scalability, security, automation, and cost-efficiency. With the rapid adoption of AI, edge computing, and hybrid cloud models, organizations must take a proactive approach to modernizing their infrastructure. This blog explores how companies can future-proof their data centers to ensure long-term success in an ever-changing technological landscape.
## Introduction
Data centers are the backbone of modern IT operations, housing the critical infrastructure that powers businesses worldwide. However, the traditional approach to data center management is becoming obsolete as enterprises move towards hybrid, multi-cloud, and edge computing models. The shift is driven by the need for greater agility, scalability, and efficiency while maintaining robust security and cost control.
Organizations that fail to evolve their data center strategies risk facing performance bottlenecks, security vulnerabilities, and rising operational costs. Future-proofing your data center involves strategic planning, modernization efforts, and adopting emerging technologies that can handle future IT demands.
## Benefits
A well-planned data center strategy ensures that organizations stay agile, competitive, and resilient in the face of technological disruptions. Below are some key benefits of future-proofing your data center:
### 1. Scalability & Flexibility
With the rapid growth of big data, AI workloads, and remote work, companies need data centers that scale effortlessly. Future-proofing your infrastructure ensures:
- Cloud & Hybrid Solutions: The ability to dynamically scale workloads between on-premise and cloud environments.
- Containerization & Microservices: Technologies like Kubernetes allow flexible, lightweight application deployments.
- Edge Computing Integration: Deploying resources closer to users to reduce latency and enhance real-time processing.
### 2. Cost Optimization & Energy Efficiency
Rising energy costs and environmental concerns push organizations to adopt efficient and sustainable data center models. Strategies include:
- Green Computing Initiatives: Using renewable energy sources and energy-efficient hardware.
- AI-Driven Resource Management: Automating cooling and power usage based on workload demand.
- Server Consolidation: Reducing excess hardware to minimize operational expenses.
### 3. Enhanced Security & Compliance
Cybersecurity threats continue to evolve, making it critical to fortify data centers against attacks. Future-proofing involves:
- Zero-Trust Architecture: Ensuring continuous authentication and verification for users and devices.
- AI-Powered Security: Using machine learning to detect anomalies and prevent breaches.
- Regulatory Compliance: Meeting GDPR, HIPAA, and ISO 27001 standards to avoid fines and reputational damage.
### 4. Automation & AI-Driven Management
As IT workloads grow, manual management becomes unsustainable. Automating infrastructure can:
- Reduce Downtime: AI-driven predictive maintenance helps identify failures before they occur.
- Optimize Workloads: Automated load balancing improves resource allocation.
- Self-Healing Systems: AI-powered automation restarts and reconfigures services automatically in case of failures.
## Challenges
Despite the clear benefits, modernizing a data center comes with its own set of challenges:
### 1. High Migration Costs & Complexity
Moving workloads from legacy systems to cloud and hybrid models can be expensive. Organizations must:
- Conduct cost-benefit analyses before migrating.
- Implement a phased migration strategy to reduce downtime.
- Train IT teams on cloud-native architectures.
### 2. Security Risks in a Hybrid Environment
Hybrid and multi-cloud environments introduce new security risks, such as:
- Data leakage due to misconfigured cloud settings.
- Expanded attack surface across multiple environments.
- Compliance challenges in managing data across jurisdictions.
### 3. Ensuring Business Continuity During Transition
Shifting to a modernized data center can disrupt operations if not managed carefully. To mitigate risks:
- Implement disaster recovery (DR) and backup plans.
- Use redundant architectures to minimize service interruptions.
- Test infrastructure updates in sandbox environments before deployment.
## Conclusion
A future-proof data center is more than just an IT investment—it’s a strategic advantage. By integrating scalable infrastructure, security enhancements, automation, and cost-effective energy solutions, organizations can stay ahead of technological shifts.
To remain resilient and competitive, businesses must:
- Adopt hybrid and cloud solutions for agility.
- Leverage automation and AI to improve efficiency.
- Enhance security measures to protect critical assets.
- Optimize costs with energy-efficient strategies.
The future of IT infrastructure is here—will your data center be ready? Stay tuned for more insights on IT transformation and infrastructure evolution in upcoming blogs!
 Greener Datacenters – How IT Leaders Can Drive Energy-Efficient Infrastructure
Greener Datacenters – How IT Leaders Can Drive Energy-Efficient Infrastructure
Datacenters are the digital engines powering everything from cloud applications to AI workloads—but they come at a cost: energy consumption. With sustainability now a board-level concern, IT leaders must rethink how datacenters are designed, operated, and optimized. This post explores the strategies that can make datacenter infrastructure greener, more efficient, and future-ready.
## Introduction
As digital demand rises, so does the environmental footprint of datacenters. These facilities account for 1-2% of global electricity consumption—a number expected to grow. With ESG commitments and operational costs under scrutiny, it’s time to shift from energy-hungry architectures to energy-efficient, sustainable datacenters.
## 1. The Business Case for Green Datacenters
Going green isn’t just ethical—it’s smart business:
- Lower energy costs
- Enhanced brand reputation
- Support for regulatory compliance and ESG goals
- Eligibility for green financing and incentives
Sustainability is no longer a checkbox—it’s a differentiator.
### 2. Key Technologies Enabling Energy Efficiency
- Liquid Cooling Systems – Use less power than traditional air cooling.
- AI-Driven Power Optimization – Dynamically adjust workloads and cooling systems.
- Server Virtualization & Consolidation – Reduces hardware footprint and energy draw.
- Energy-Efficient UPS & Power Distribution Units (PDUs) – Minimize loss during energy conversion.
### 3. Sustainable Design & Architecture
- Modular Datacenter Design – Scalable and built to spec, minimizing excess capacity.
- Use of Renewable Energy – Solar, wind, and hydro to offset carbon emissions.
- Site Selection – Cooler climates and access to green power reduce operational loads.
- Green Building Certifications – LEED or ISO 50001 for sustainability benchmarks.
### 4. Metrics That Matter
Measure what you manage. Key green metrics include:
- PUE (Power Usage Effectiveness) – Ideal: <1.2
- WUE (Water Usage Effectiveness) – Monitor water consumption per kWh
- Carbon Usage Effectiveness (CUE) – Track total emissions associated with power use
- Energy Reuse Effectiveness (ERE) – Captures how much energy is recycled
### Best Practices for IT Leaders
- Audit and Benchmark – Conduct regular energy audits.
- Design for Sustainability from Day One – Embed green thinking into procurement and architecture.
- Collaborate with Facilities Teams – Energy savings come from IT + operations alignment. 📌 Educate Teams – Make energy awareness part of the culture.
## Conclusion
Greener datacenters are not a trend—they’re a business imperative. From energy savings to regulatory compliance and competitive advantage, sustainability is reshaping how IT infrastructure is planned and delivered. IT leaders who act now can reduce costs, cut emissions, and position their organizations for a resilient, responsible digital future.
 The Rise of Edge Computing – How It’s Transforming Data Centers
The Rise of Edge Computing – How It’s Transforming Data Centers
Traditional data centers are under pressure as businesses demand faster processing, lower latency, and real-time analytics. Edge computing is reshaping the landscape by decentralizing processing, reducing bandwidth costs, and enhancing system responsiveness. Understanding its impact is crucial for IT decision-makers.
## Introduction
As AI, IoT, and real-time applications become mainstream, traditional cloud data centers face scalability challenges. Edge computing offers a decentralized alternative, processing data closer to the source to reduce latency and bandwidth dependency.
## 1. What is Edge Computing?
- ✅ Decentralized processing near data sources (IoT devices, sensors, etc.).
- ✅ Reduces latency for real-time analytics and automation.
- ✅ Minimizes bandwidth costs by reducing cloud data transfers.
## 2. Why Edge Computing is Critical for Modern IT Infrastructure
- 📌 Faster Decision-Making – Critical for industries like healthcare, manufacturing, and - smart cities. -
- 📌 Lower Bandwi- dth Costs – Reduces dependency on cloud-based data transfers.
- 📌 Enhanced Security – Processes sensitive data locally rather than in the cloud.
## 3. How Edge Computing Transforms Data Centers
- ✅ Hybrid Data Center Models – Combining centralized cloud with edge nodes.
- ✅ AI & IoT Integration – Processing massive real-time data streams.
- ✅ Scalability & Reliability – Expanding capacity without latency issues.
## Conclusion
Edge computing isn’t replacing traditional data centers—it’s augmenting them. Future-ready IT infrastructures must incorporate edge architectures to ensure agility, performance, and cost efficiency.
 The Role of IT Project Management in Business Success
The Role of IT Project Management in Business Success
Effective IT project management is essential for delivering successful digital transformations, infrastructure upgrades, and software development. Without proper methodologies, projects risk budget overruns, delays, and misalignment with business objectives. This blog highlights the importance of IT project management, its benefits, and the challenges organizations face in execution.
## Introduction
As businesses rely more on technology, IT projects have become central to growth and operational efficiency. However, many projects fail due to poor planning, lack of resources, or weak execution strategies. Implementing strong project management frameworks ensures on-time, on-budget, and high-quality project delivery.
## Benefits
- Improved Execution & Delivery: Clear timelines, roles, and milestones reduce project risks.
- Better Resource Allocation: Ensures teams work efficiently and within budget.
- Alignment with Business Goals: Ensures projects contribute to overall company success.
- Risk Mitigation: Identifying potential failures early prevents costly rework.
## Challenges
- Scope Creep: Uncontrolled expansion of project requirements.
- Lack of Communication: Misalignment between stakeholders leads to project delays.
- Budget Constraints: Ensuring financial efficiency without compromising project quality.
## Conclusion
Strong IT project management ensures strategic execution, better efficiency, and high-value delivery. By adopting the right methodologies, businesses can maximize success. Stay tuned for practical insights on IT project methodologies in upcoming posts!
 Enterprise Architecture - The Silent Force Driving Organizational Efficiency
Enterprise Architecture - The Silent Force Driving Organizational Efficiency
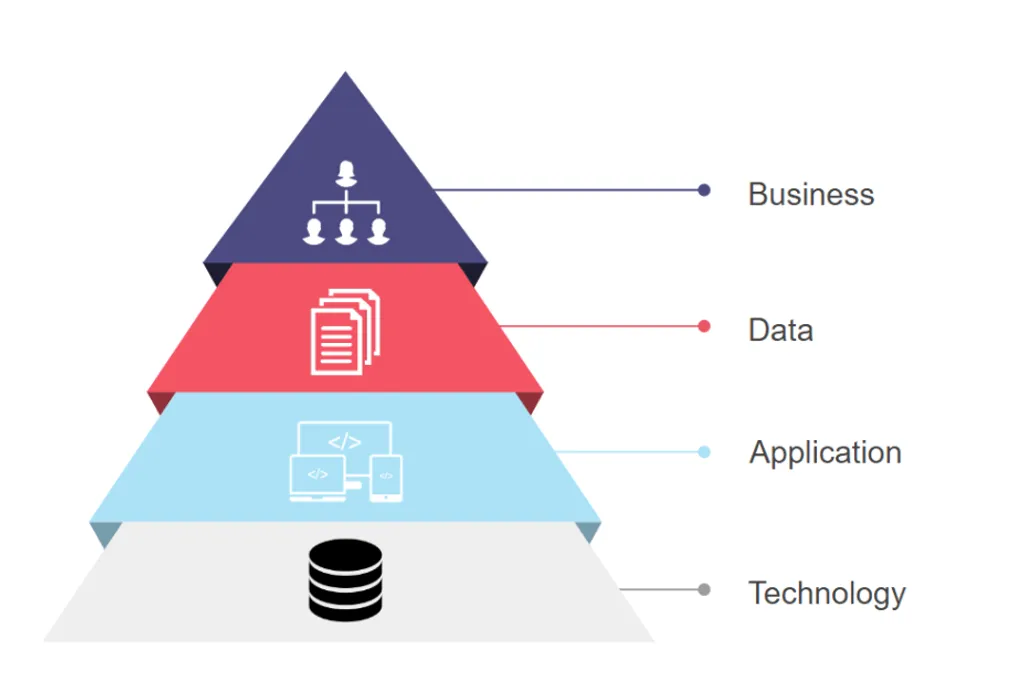
Enterprise Architecture (EA) is a strategic enabler that aligns technology, processes, and resources with business goals. By enhancing visibility, promoting resource reusability, and clarifying ownership, EA drives operational efficiency, cost savings, and innovation. This article explores the critical role of EA in modern organizations, the benefits it delivers, common challenges, and how to embed it as a core component of business strategy.
## Introduction
In today’s fast-paced digital landscape, organizations are constantly seeking ways to streamline operations, cut costs, and accelerate innovation. Yet many overlook a critical enabler that works quietly in the background: Enterprise Architecture (EA). Far beyond technical frameworks and IT blueprints, EA plays a strategic role in maximizing resource visibility, eliminating duplication, and mapping clear ownership across the enterprise. Its true power lies in connecting business goals with technology investments, ensuring that every move is intentional, efficient, and value-driven.
## The Role of Enterprise Architecture
### 1. Enhancing Resource Visibility
Enterprise Architecture brings all organizational assets — systems, data, processes, capabilities — into a single, clear view. By doing so, decision-makers can identify underused assets, recognize opportunities for optimization, and make data-driven investment choices. Visibility not only reduces waste but also empowers faster, smarter decision-making.
### 2. Promoting Reusability and Eliminating Duplicates
In many organizations, different departments often end up purchasing or developing redundant systems because of siloed operations. EA acts as the bridge that connects these silos, promoting the reusability of existing platforms, components, and services. This prevents unnecessary duplication, saving significant costs and reducing operational complexity.
### 3. Clarifying Resource Ownership
Enterprise Architecture provides a clear mapping of resource ownership across the organization. It defines who is responsible for what, creating transparency and accountability. This clarity supports better governance, accelerates problem resolution, and ensures that resources are managed proactively rather than reactively.
## Business Benefits
When implemented effectively, EA delivers a range of business benefits:
- Cost Savings: By eliminating duplicate purchases and optimizing resource usage.
- Operational Efficiency: By aligning technology with business strategy and simplifying processes.
- Innovation Acceleration: By freeing up resources that can be reallocated to growth initiatives.
- Risk Reduction: By ensuring better compliance, security, and continuity through clear ownership and governance.
EA transforms from a back-office function into a strategic powerhouse that fuels competitive advantage.
## Challenges and Misconceptions
Despite its value, EA often faces resistance due to misconceptions. Some view it as purely technical or overly bureaucratic. Others mistakenly see it as an optional luxury rather than a strategic necessity. Successful EA initiatives address these misconceptions by:
- Communicating the business value of EA in clear terms.
- Integrating EA into everyday decision-making, not just long-term planning.
- Keeping EA agile and responsive to changing business needs.
Enterprise Architecture must be seen as a living practice — evolving alongside the organization, not a one-time project.
## Conclusion
In a world where agility, efficiency, and strategic foresight are critical for survival, Enterprise Architecture emerges as a silent but powerful driver of success. It connects the dots between resources, technology, and business goals, ensuring that organizations not only survive but thrive in the face of constant change.
Investing in Enterprise Architecture is not just an IT decision — it is a strategic business imperative.
Ready to unlock the true potential of Enterprise Architecture? Start by making it a core part of your business strategy today.
 Why Project Governance Is the Missing Link in Most IT Failures
Why Project Governance Is the Missing Link in Most IT Failures
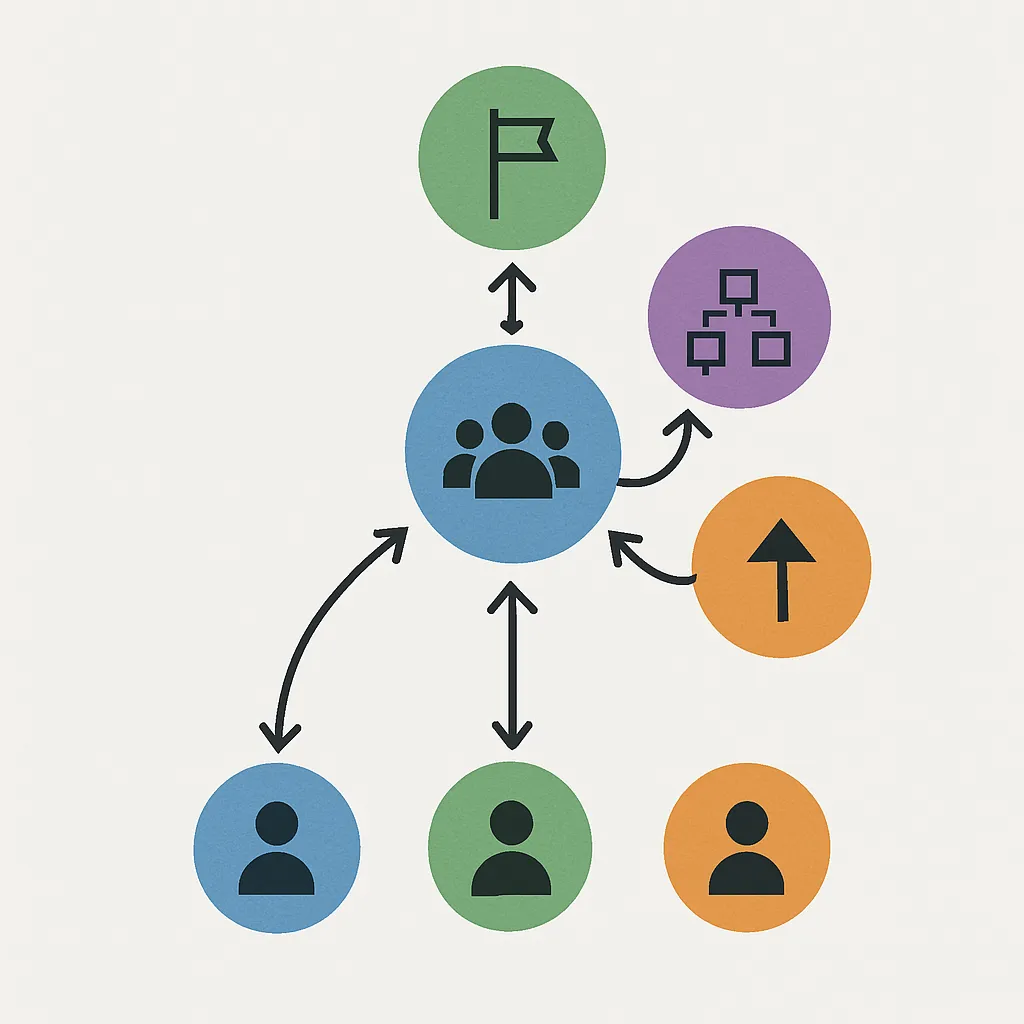
While methodologies like Agile and Scrum dominate the IT project management conversation, project governance is often the silent factor determining success or failure. Project governance isn’t about bureaucracy—it’s about structure, accountability, and strategic alignment. This post dives into how project governance can prevent common IT failures and build a foundation for scalable success.
## Introduction
Many IT projects fail—not due to technical issues or lack of methodology—but because of poor governance. Budgets spiral, timelines drift, and deliverables shift. These symptoms often stem from a lack of clear roles, decision-making frameworks, and strategic oversight. Strong governance is the backbone of successful IT delivery.
## 1. What Is Project Governance?
Project governance is the framework that guides decision-making, accountability, and control throughout a project lifecycle. It includes:
- Defined roles and responsibilities (sponsor, steering committee, PMO)
- Escalation paths for issues and risks
- Change control processes and performance metrics
## 2. Why Governance Often Gets Overlooked
- Focus shifts to delivery speed over structure.
- Teams assume Agile frameworks alone are enough.
- Governance is seen as administrative overhead.
In reality, a lightweight governance model supports agility while protecting projects from chaos.
## 3. Key Benefits of Strong Project Governance
- Clear Accountability – Everyone knows who makes decisions and owns outcomes.
- Strategic Alignment – Projects stay aligned with business goals and priorities.
- Early Risk Detection – Escalation paths and governance reviews surface issues sooner.
- Stakeholder Confidence – Transparent reporting builds trust with leadership.
## 4. Practical Governance Models
- Steering Committees – Provide strategic oversight and unblock major decisions.
- RAID Logs – Track Risks, Assumptions, Issues, and Dependencies.
- Stage Gates – Milestone reviews for scope, budget, and progress validation.
- PMO Involvement – Enable consistent practices and coaching across projects.
## 5. Balancing Governance with Agility
Governance doesn’t mean waterfall. Modern governance can be adaptive:
- Set guardrails, not gates.
- Use weekly health checks instead of rigid templates.
- Empower teams with decision rights within defined boundaries.
## Conclusion
If Agile is the engine, project governance is the steering wheel. Without it, IT projects veer off course. Strong governance ensures strategic alignment, stakeholder trust, and scalable delivery—without slowing innovation. It’s time governance got the attention it deserves in every IT project playbook.
 Choosing the Right Project Management Approach
Choosing the Right Project Management Approach 






