 Choosing the Right Project Management Approach
Choosing the Right Project Management Approach
Project management methodologies define the success of IT projects. While Agile offers flexibility and adaptability, Waterfall provides structure and predictability. The key to effective IT project execution is selecting the right approach based on project scope, team dynamics, and business objectives.
## Introduction
Choosing between Agile and Waterfall is a critical decision in IT project management. Agile promotes iteration and flexibility, while Waterfall emphasizes structured phases and documentation. Understanding the strengths and limitations of each helps organizations optimize project execution.
## 1. Agile: Flexibility & Rapid Adaptation
Agile methodologies (Scrum, Kanban) enable teams to iterate quickly, making adjustments as needed.
- Best for dynamic projects with changing requirements.
- Focus on collaboration and continuous feedback.
- Delivers incremental value rather than waiting until project completion.
## 2. Waterfall: Structured & Predictable Execution
Waterfall follows a linear approach where each phase is completed before moving to the next.
- Ideal for well-defined projects with fixed requirements.
- Clear documentation & compliance for regulated industries.
- Strong project control with defined scope and timelines.
## 3. When to Choose Agile vs. Waterfall
### Use Agile when:
- Requirements are evolving.
- Speed and flexibility are critical.
- Frequent stakeholder feedback is required.
### Use Waterfall when:
- Project scope is clear and stable.
- Compliance and documentation are key.
- The budget and timeline must be strictly controlled.
## 4. Hybrid Approaches: Best of Both Worlds
Many organizations adopt a Hybrid model, combining Agile’s adaptability with Waterfall’s structure.
- Agile for development phases.
- Waterfall for planning & compliance.
- Ensures both flexibility and predictability.
## Conclusion
No single approach fits all projects. IT leaders must align methodologies with project scope, risk tolerance, and business needs. A well-chosen framework maximizes efficiency, mitigates risks, and drives successful project delivery.
 The Role of IT Project Management in Business Success
The Role of IT Project Management in Business Success
Effective IT project management is essential for delivering successful digital transformations, infrastructure upgrades, and software development. Without proper methodologies, projects risk budget overruns, delays, and misalignment with business objectives. This blog highlights the importance of IT project management, its benefits, and the challenges organizations face in execution.
## Introduction
As businesses rely more on technology, IT projects have become central to growth and operational efficiency. However, many projects fail due to poor planning, lack of resources, or weak execution strategies. Implementing strong project management frameworks ensures on-time, on-budget, and high-quality project delivery.
## Benefits
- Improved Execution & Delivery: Clear timelines, roles, and milestones reduce project risks.
- Better Resource Allocation: Ensures teams work efficiently and within budget.
- Alignment with Business Goals: Ensures projects contribute to overall company success.
- Risk Mitigation: Identifying potential failures early prevents costly rework.
## Challenges
- Scope Creep: Uncontrolled expansion of project requirements.
- Lack of Communication: Misalignment between stakeholders leads to project delays.
- Budget Constraints: Ensuring financial efficiency without compromising project quality.
## Conclusion
Strong IT project management ensures strategic execution, better efficiency, and high-value delivery. By adopting the right methodologies, businesses can maximize success. Stay tuned for practical insights on IT project methodologies in upcoming posts!
 Enterprise Architecture - The Silent Force Driving Organizational Efficiency
Enterprise Architecture - The Silent Force Driving Organizational Efficiency
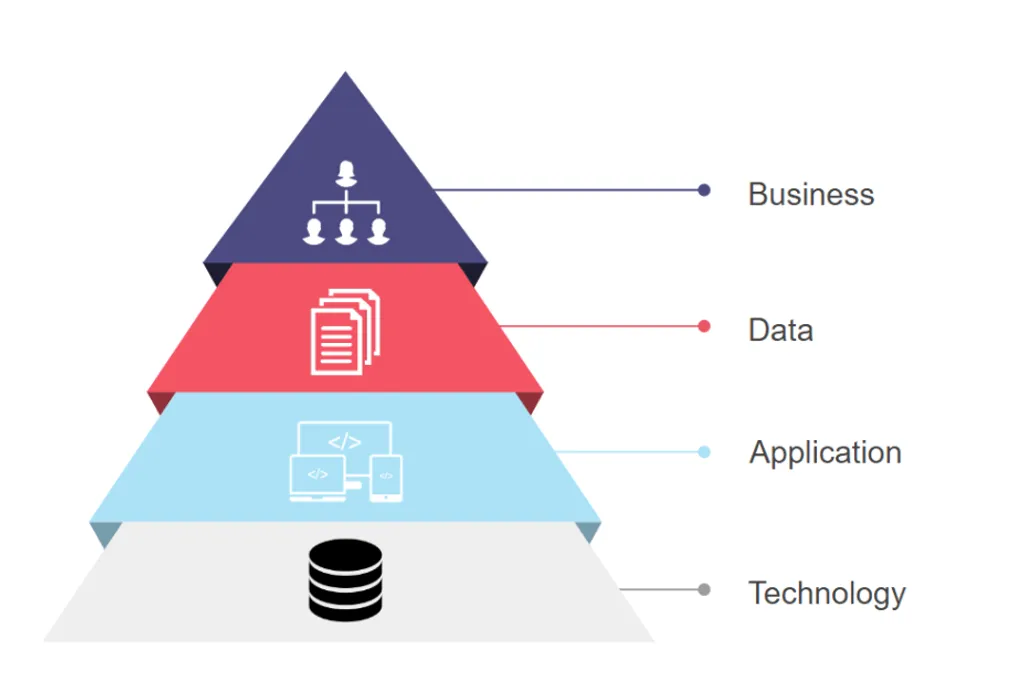
Enterprise Architecture (EA) is a strategic enabler that aligns technology, processes, and resources with business goals. By enhancing visibility, promoting resource reusability, and clarifying ownership, EA drives operational efficiency, cost savings, and innovation. This article explores the critical role of EA in modern organizations, the benefits it delivers, common challenges, and how to embed it as a core component of business strategy.
## Introduction
In today’s fast-paced digital landscape, organizations are constantly seeking ways to streamline operations, cut costs, and accelerate innovation. Yet many overlook a critical enabler that works quietly in the background: Enterprise Architecture (EA). Far beyond technical frameworks and IT blueprints, EA plays a strategic role in maximizing resource visibility, eliminating duplication, and mapping clear ownership across the enterprise. Its true power lies in connecting business goals with technology investments, ensuring that every move is intentional, efficient, and value-driven.
## The Role of Enterprise Architecture
### 1. Enhancing Resource Visibility
Enterprise Architecture brings all organizational assets — systems, data, processes, capabilities — into a single, clear view. By doing so, decision-makers can identify underused assets, recognize opportunities for optimization, and make data-driven investment choices. Visibility not only reduces waste but also empowers faster, smarter decision-making.
### 2. Promoting Reusability and Eliminating Duplicates
In many organizations, different departments often end up purchasing or developing redundant systems because of siloed operations. EA acts as the bridge that connects these silos, promoting the reusability of existing platforms, components, and services. This prevents unnecessary duplication, saving significant costs and reducing operational complexity.
### 3. Clarifying Resource Ownership
Enterprise Architecture provides a clear mapping of resource ownership across the organization. It defines who is responsible for what, creating transparency and accountability. This clarity supports better governance, accelerates problem resolution, and ensures that resources are managed proactively rather than reactively.
## Business Benefits
When implemented effectively, EA delivers a range of business benefits:
- Cost Savings: By eliminating duplicate purchases and optimizing resource usage.
- Operational Efficiency: By aligning technology with business strategy and simplifying processes.
- Innovation Acceleration: By freeing up resources that can be reallocated to growth initiatives.
- Risk Reduction: By ensuring better compliance, security, and continuity through clear ownership and governance.
EA transforms from a back-office function into a strategic powerhouse that fuels competitive advantage.
## Challenges and Misconceptions
Despite its value, EA often faces resistance due to misconceptions. Some view it as purely technical or overly bureaucratic. Others mistakenly see it as an optional luxury rather than a strategic necessity. Successful EA initiatives address these misconceptions by:
- Communicating the business value of EA in clear terms.
- Integrating EA into everyday decision-making, not just long-term planning.
- Keeping EA agile and responsive to changing business needs.
Enterprise Architecture must be seen as a living practice — evolving alongside the organization, not a one-time project.
## Conclusion
In a world where agility, efficiency, and strategic foresight are critical for survival, Enterprise Architecture emerges as a silent but powerful driver of success. It connects the dots between resources, technology, and business goals, ensuring that organizations not only survive but thrive in the face of constant change.
Investing in Enterprise Architecture is not just an IT decision — it is a strategic business imperative.
Ready to unlock the true potential of Enterprise Architecture? Start by making it a core part of your business strategy today.
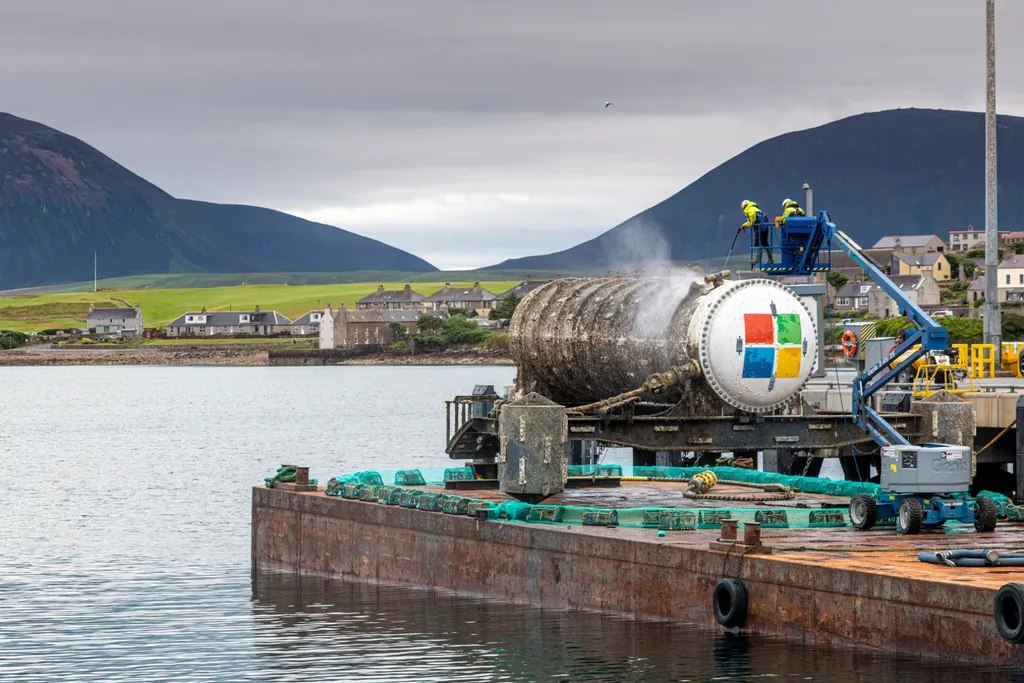 Why Microsoft Abandoned Its Successful Underwater Data Center Project
Why Microsoft Abandoned Its Successful Underwater Data Center Project
In a surprising move, Microsoft has decided to retire Project Natick—its ambitious, futuristic underwater data center initiative. Despite its promising performance and environmental benefits, the project will not see a commercial rollout. This post explores the history of Project Natick, its outcomes, and why Microsoft ultimately chose to move on.
## Introduction
In 2015, Microsoft launched one of the most daring infrastructure experiments in data center history: Project Natick, an underwater data center initiative designed to test whether data centers submerged in the ocean could be more sustainable, efficient, and reliable than their land-based counterparts. Eight years later, the project has officially been shelved—despite proving successful on many fronts.
So what went right—and why did Microsoft walk away?
## The History of Project Natick
Project Natick began as a response to multiple challenges:
- The rising demand for low-latency data delivery.
- Growing concerns around energy usage and sustainability in data centers.
- The desire to deploy data centers closer to coastal population hubs.
### Phase 1 (2015):
Microsoft submerged a prototype off the coast of California. This capsule operated for 105 days and proved the feasibility of submersion without disruption.
### Phase 2 (2018-2020):
A larger vessel was placed 117 feet deep off the coast of Orkney Islands, Scotland. This version contained 864 servers and 27.6 petabytes of storage and was fully powered by renewable energy from wind and tidal sources.
The capsule operated for over two years without issues, outperforming traditional data centers in terms of reliability and sustainability.
## Outcomes of the Project
Project Natick was not a failed experiment—in fact, it was a remarkable success.
### ✅ Higher Reliability
Microsoft reported that the underwater data center had one-eighth the failure rate of its land-based counterparts. The reduced exposure to human error, corrosion, and temperature fluctuation contributed to this reliability.
### ✅ Environmental Efficiency
- Powered entirely by renewable energy.
- Naturally cooled by seawater, eliminating the need for traditional HVAC systems.
- Reduced carbon footprint and energy costs.
### ✅ Modular & Rapid Deployment
- Data centers could be manufactured, shipped, and deployed within 90 days.
- Ideal for regions with limited space or infrastructure.
### ✅ Proximity to Coastal Populations
- Almost 50% of the global population lives near the coast.
- Underwater data centers could reduce latency and improve connectivity.
## So Why Did Microsoft Abandon It?
Despite its many advantages, Microsoft quietly announced it would not pursue commercial-scale underwater data centers.
Here’s why:
### ❌ Scalability Limitations
- While modular, the pods had a fixed capacity and weren’t easily upgradable or serviceable.
- Scaling would require deploying many units in marine environments, adding logistical and environmental complexity.
### ❌ Maintenance Challenges
- Physical repairs meant bringing the entire unit back to the surface.
- Long-term maintenance and lifecycle planning were not as flexible as with land-based facilities.
### ❌ Regulatory and Environmental Hurdles
- Deploying in coastal waters requires governmental and environmental permissions.
- Potential ecological concerns and jurisdictional red tape presented barriers to global rollout.
### ❌ Cloud Strategy Shift
- Microsoft is doubling down on AI, hybrid cloud, and edge computing, which favor more dynamic, accessible infrastructure.
- Underwater pods, while innovative, don’t align well with the rapid scaling needs of AI model training and inference.
## Conclusion
Project Natick may be over, but it left a lasting impact. It proved that sustainable, resilient, and low-maintenance data centers are possible—even underwater. It offered insight into how modular design, renewable power, and remote operations can shape future infrastructure.
As Microsoft pivots toward AI and global edge computing, Natick will be remembered as an inspiring leap toward sustainable cloud infrastructure. Sometimes, even the most successful pilots don’t make it to production—but their lessons carry forward.
 Why Project Governance Is the Missing Link in Most IT Failures
Why Project Governance Is the Missing Link in Most IT Failures
While methodologies like Agile and Scrum dominate the IT project management conversation, project governance is often the silent factor determining success or failure. Project governance isn’t about bureaucracy—it’s about structure, accountability, and strategic alignment. This post dives into how project governance can prevent common IT failures and build a foundation for scalable success.
## Introduction
Many IT projects fail—not due to technical issues or lack of methodology—but because of poor governance. Budgets spiral, timelines drift, and deliverables shift. These symptoms often stem from a lack of clear roles, decision-making frameworks, and strategic oversight. Strong governance is the backbone of successful IT delivery.
## 1. What Is Project Governance?
Project governance is the framework that guides decision-making, accountability, and control throughout a project lifecycle. It includes:
- Defined roles and responsibilities (sponsor, steering committee, PMO)
- Escalation paths for issues and risks
- Change control processes and performance metrics
## 2. Why Governance Often Gets Overlooked
- Focus shifts to delivery speed over structure.
- Teams assume Agile frameworks alone are enough.
- Governance is seen as administrative overhead.
In reality, a lightweight governance model supports agility while protecting projects from chaos.
## 3. Key Benefits of Strong Project Governance
- Clear Accountability – Everyone knows who makes decisions and owns outcomes.
- Strategic Alignment – Projects stay aligned with business goals and priorities.
- Early Risk Detection – Escalation paths and governance reviews surface issues sooner.
- Stakeholder Confidence – Transparent reporting builds trust with leadership.
## 4. Practical Governance Models
- Steering Committees – Provide strategic oversight and unblock major decisions.
- RAID Logs – Track Risks, Assumptions, Issues, and Dependencies.
- Stage Gates – Milestone reviews for scope, budget, and progress validation.
- PMO Involvement – Enable consistent practices and coaching across projects.
## 5. Balancing Governance with Agility
Governance doesn’t mean waterfall. Modern governance can be adaptive:
- Set guardrails, not gates.
- Use weekly health checks instead of rigid templates.
- Empower teams with decision rights within defined boundaries.
## Conclusion
If Agile is the engine, project governance is the steering wheel. Without it, IT projects veer off course. Strong governance ensures strategic alignment, stakeholder trust, and scalable delivery—without slowing innovation. It’s time governance got the attention it deserves in every IT project playbook.
 Choosing the Right Project Management Approach
Choosing the Right Project Management Approach 



