 Enterprise Architecture - The Silent Force Driving Organizational Efficiency
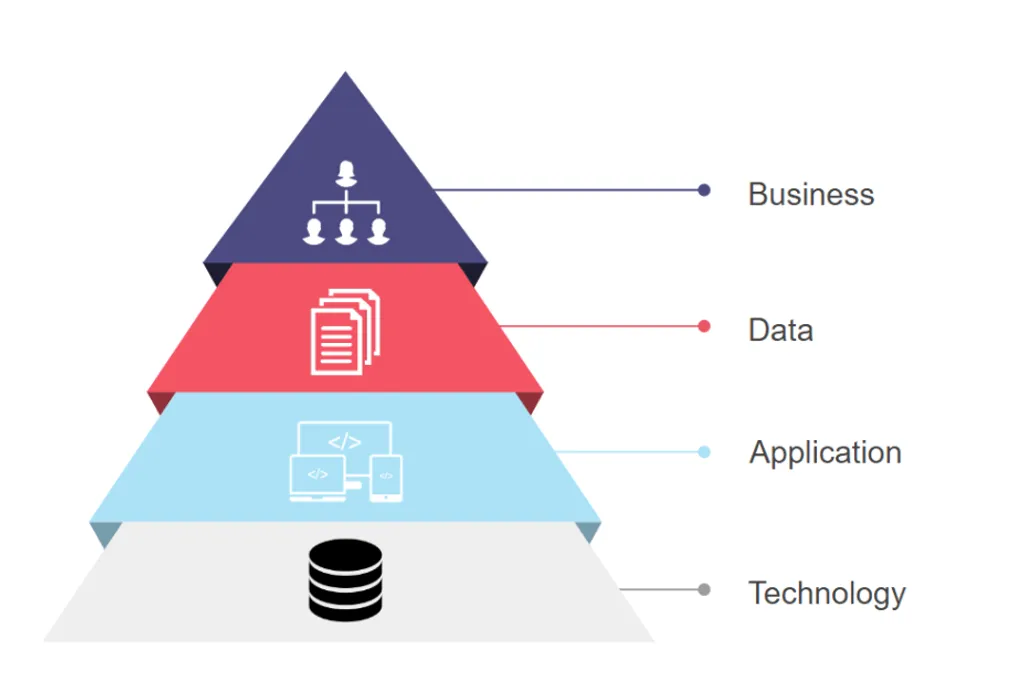
Enterprise Architecture - The Silent Force Driving Organizational Efficiency Enterprise Architecture (EA) is a strategic enabler that aligns technology, processes, and resources with business goals. By enhancing visibility, promoting resource reusability, and clarifying ownership, EA drives operational efficiency, cost savings, and innovation. This article explores the critical role of EA in modern organizations, the benefits it delivers, common challenges, and how to embed it as a core component of business strategy. ## Introduction In today’s fast-paced digital landscape, organizations are constantly seeking ways to streamline operations, cut costs, and accelerate innovation. Yet many overlook a critical enabler that works quietly in the background: Enterprise Architecture (EA). Far beyond technical frameworks and IT blueprints, EA plays a strategic role in maximizing resource visibility, eliminating duplication, and mapping clear ownership across the enterprise. Its true power lies in connecting business goals with technology investments, ensuring that every move is intentional, efficient, and value-driven. ## The Role of Enterprise Architecture ### 1. Enhancing Resource Visibility Enterprise Architecture brings all organizational assets — systems, data, processes, capabilities — into a single, clear view. By doing so, decision-makers can identify underused assets, recognize opportunities for optimization, and make data-driven investment choices. Visibility not only reduces waste but also empowers faster, smarter decision-making. ### 2. Promoting Reusability and Eliminating Duplicates In many organizations, different departments often end up purchasing or developing redundant systems because of siloed operations. EA acts as the bridge that connects these silos, promoting the reusability of existing platforms, components, and services. This prevents unnecessary duplication, saving significant costs and reducing operational complexity. ### 3. Clarifying Resource Ownership Enterprise Architecture provides a clear mapping of resource ownership across the organization. It defines who is responsible for what, creating transparency and accountability. This clarity supports better governance, accelerates problem resolution, and ensures that resources are managed proactively rather than reactively. ## Business Benefits When implemented effectively, EA delivers a range of business benefits: - Cost Savings: By eliminating duplicate purchases and optimizing resource usage. - Operational Efficiency: By aligning technology with business strategy and simplifying processes. - Innovation Acceleration: By freeing up resources that can be reallocated to growth initiatives. - Risk Reduction: By ensuring better compliance, security, and continuity through clear ownership and governance. EA transforms from a back-office function into a strategic powerhouse that fuels competitive advantage. ## Challenges and Misconceptions Despite its value, EA often faces resistance due to misconceptions. Some view it as purely technical or overly bureaucratic. Others mistakenly see it as an optional luxury rather than a strategic necessity. Successful EA initiatives address these misconceptions by: - Communicating the business value of EA in clear terms. - Integrating EA into everyday decision-making, not just long-term planning. - Keeping EA agile and responsive to changing business needs. Enterprise Architecture must be seen as a living practice — evolving alongside the organization, not a one-time project. ## Conclusion In a world where agility, efficiency, and strategic foresight are critical for survival, Enterprise Architecture emerges as a silent but powerful driver of success. It connects the dots between resources, technology, and business goals, ensuring that organizations not only survive but thrive in the face of constant change. Investing in Enterprise Architecture is not just an IT decision — it is a strategic business imperative. Ready to unlock the true potential of Enterprise Architecture? Start by making it a core part of your business strategy today.
